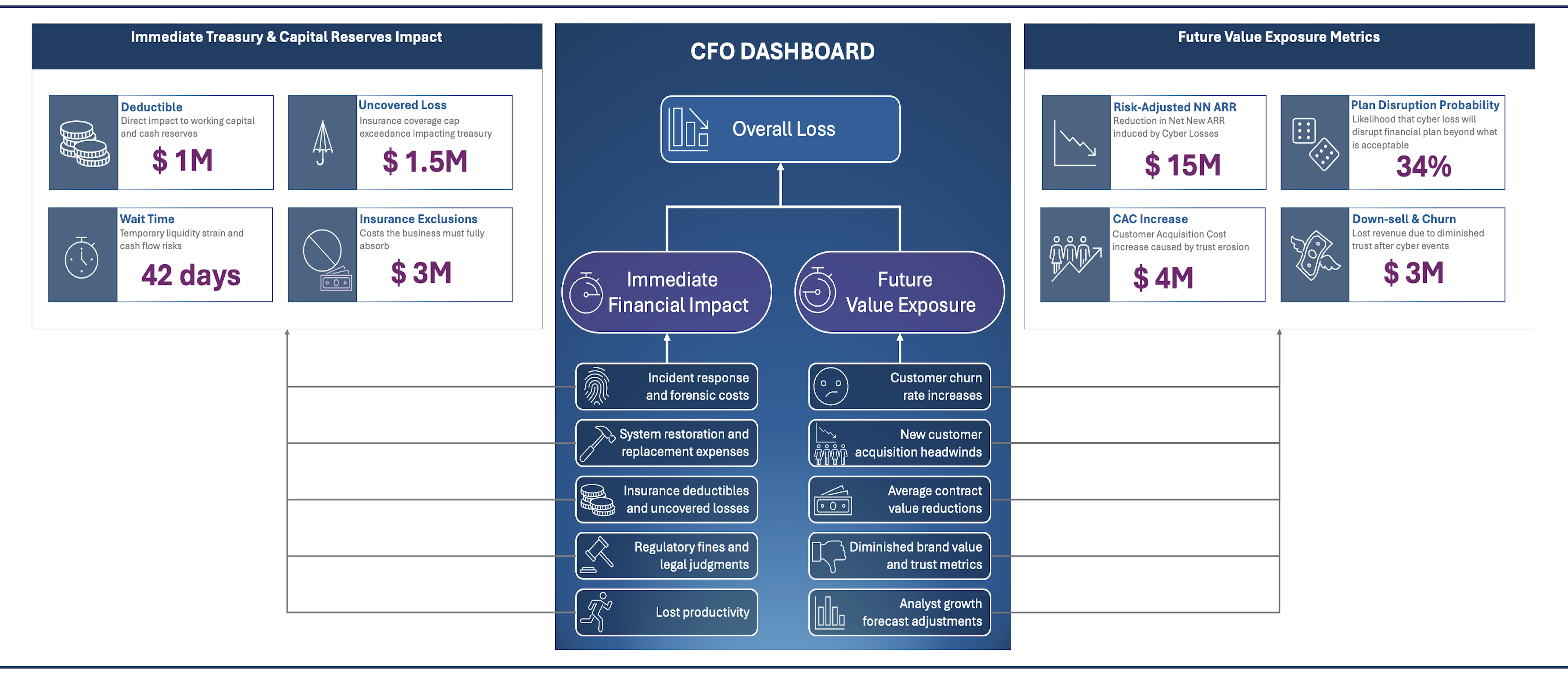
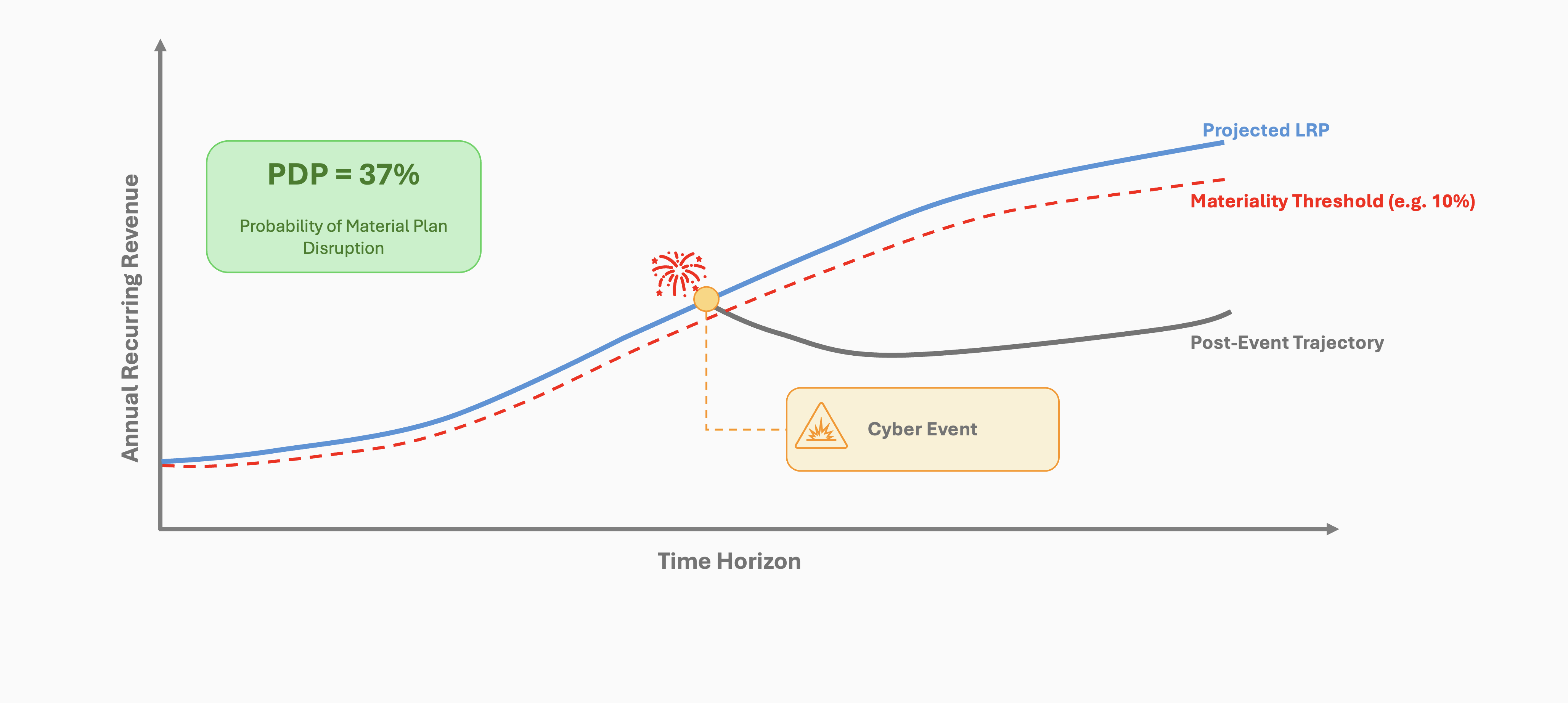
· Dayo Adetoye (PhD, C|CISO) · Reducing Friction and Accelerating Innovation · 5 min read
Beyond the Firefighting:
Enable Risk Improvement through Proactive Capacity Planning.
Security teams are often trapped in reactive cycles, firefighting incidents instead of addressing root causes or improving resilience. Gain strategic insight that helps you elevate your team's impact by unlocking time for proactive risk reduction and long-term improvement.

Question:
- What percentage of your team’s time is dedicated to reducing future risk?
- Can you estimate the likelihood that your team has the capacity for substantial improvement work?
Premise:
- Security teams are often trapped in reactive cycles, firefighting incidents instead of addressing root causes or improving resilience.
- Effective capacity planning can break this cycle, enabling teams to invest time in risk improvement while maintaining operational excellence.
Value Proposition:
This article introduces a simple yet effective method for calculating and estimating capacity, offering actionable insights to optimize resource allocation and prioritize work. By leveraging this approach, your team can transition from reactive firefighting to proactive planning, reducing long-term risks and enhancing security outcomes.
Ready to Dive In?
Jump straight to our free calculator below to estimate your team’s proactive capacity.
Why Teams Get Stuck in Firefighting Mode
Tech Debt Theater
In the theater of tech debt, reactive work is both the actor and the stage - capacity planning is the exit door.
- Limited time for proactive initiatives such as patching, automation, and process improvement. These are the types of projects that capacity planning can support, making it crucial to break the cycle of technical debt that fuels reactive workloads.
- High volume of reactive work driven by constant incidents.
- Lack of visibility into team capacity and workload dynamics.
Calculating Proactive Capacity
Proactive Capacity represents the portion of a team’s resources available for forward-looking initiatives that reduce future risks and drive strategic improvements, rather than being consumed by reactive tasks. Estimating the probability of sufficient proactive capacity is essential to ensure your team can meet long-term security objectives.
Here’s how proactive capacity is calculated:
Where:
- Reactive Workload: The total time spent on reactive tasks (e.g. incident response, architecture review or pen-testing), measured in hours.
- Team Capacity: The total available working time, adjusted for factors like vacations, sick leave, and other commitments.
Estimating Reactive Workload
Reactive workload represents the total time spent addressing unplanned, and other expected incoming events. It is calculated as:
Where:
- Work-Event Arrival Rate (WAR): The frequency of new events requiring team attention, typically measured in events per day or week.
- Work-Event Effort Time (WET): The average time spent processing and resolving each event, including all associated activities, measured in hours.
This formula highlights the relationship between how often events occur and the effort required to manage them. Understanding these factors enables teams to quantify their reactive workload and identify opportunities for optimizing time allocation.
Estimating Team Capacity
Team capacity reflects the total available working time, adjusted for real-world factors like vacations, sick leave, and other commitments. Recognizing that uncertainty is inevitable, we incorporate a confidence level to account for variability in these estimates. Use the calculator below to experiment with different values and observe how they influence your team’s capacity.
Proactive Capacity Calculator
This calculator performs a Monte Carlo simulation of your team’s reactive workload and team capacity, allowing you to estimate your team’s proactive capacity and the likelihood that your team has the capacity for substantial improvement work.
Proactive Probability Exceedance Proactive Capacity Target
Supporting Decision-Making
By understanding the factors that affect your team’s proactive capacity, you gain insight into the “levers” you can pull to optimize your team’s effectiveness at managing your organization’s future risk.
For example, a high work-event arrival rate may indicate the need for intervention to address the root cause of frequent events. Introducing an effective patch management process can reduce the occurrence of vulnerabilities, while implementing a robust Secure Development Lifecycle (SDLC) program can proactively address security flaws earlier in the development process, reducing event volume.
If the real driver of low proactive capacity is the time it takes to process work events, opportunities to improve this metric may include:
- Automation: Leveraging tools to streamline repetitive or time-consuming tasks.
- Process Improvements: Simplifying workflows or removing bottlenecks in existing procedures.
- AI Integration: Deploying AI to assist with threat detection, triage, and decision-making.
- Outsourcing: Delegating specific tasks to external partners, such as Managed Security Service Providers (MSSPs), to free up internal resources.
Bringing It All Together
Understanding and quantifying your proactive capacity allows you to make data-driven decisions that balance the demands of today’s reactive workload with the need to build resilience and reduce future risk.
By regularly measuring your team’s proactive capacity and modeling its drivers, you can:
- Identify Improvement Opportunities: Pinpoint specific areas where changes will have the most significant impact on capacity.
- Justify Resource Investments: Use data to advocate for additional headcount, tooling, or external support.
- Proactively Manage Risk: Ensure that your team has enough bandwidth to focus on forward-looking initiatives, such as improving processes, automating tasks, and building organizational resilience.
Proactive Capacity isn’t just a metric—it’s a strategic tool for transforming how your team operates and ensuring your organization stays ahead of emerging threats. By shifting focus from firefighting to proactive risk reduction, you position your security program as a driver of long-term success.
Call to Action
Start by measuring your team’s current proactive capacity. Use the insights gained to create a plan for improving efficiency and tackling the root causes of a low proactive capacity. Remember, the goal isn’t perfection—it’s continuous improvement that empowers your team to make meaningful progress toward reducing risk and enhancing security outcomes.